Understanding an Erection
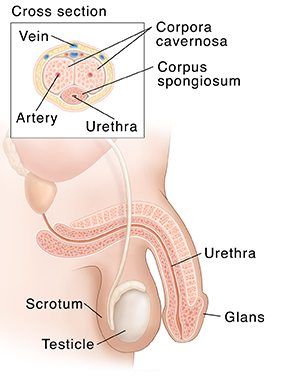
The penis is made up of spongy tissue that holds blood. When the penis is soft, blood flows in and out of the tissue. During sexual excitement, extra blood flows into the tissue. The extra blood makes the tissue swell. The penis then becomes hard (erect). This makes it firm enough to have sex. Read more about the stages of an erection below.
Stages of an erection
An erection requires a healthy mind-body team effort led by the brain. First, the brain sends out signals. Then, the blood vessels, nerves, and hormones work together to create and keep an erection.
The soft penis
When a person assigned male at birth isn't aroused, then the brain, nerves, blood vessels, and hormones won't start working to cause an erection. The amount of blood flowing into the penis's spongy chambers (corpora cavernosa and corpus spongiosum) equals the amount flowing out. The penis stays soft.
The swollen penis
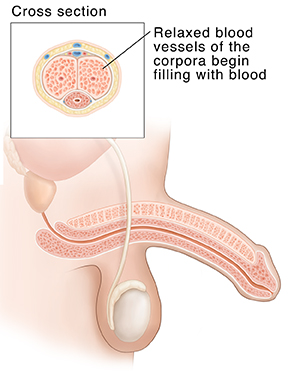
A person gets aroused by their senses. This includes sight and touch. And it includes thoughts, such as memories or fantasies. During arousal, messages brought by nerves cause the blood vessels and spongy chambers to open up (dilate). More blood flows into the penis than flows out. The penis starts to swell.
The erect penis
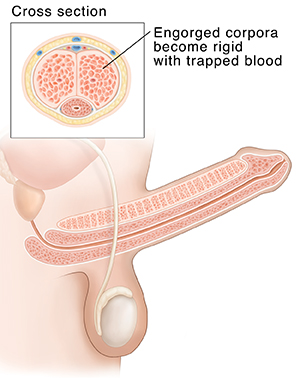
As arousal continues, nerves keep carrying messages between the penis and brain. Blood keeps moving into the man's penis. Blood-swollen tissues press against the veins. Some of the blood is kept from flowing back out. Filled with blood, the penis becomes hard. The person is able to have sex.
When there’s a problem
Physical problems or emotional issues can keep the tissue in the penis from filling with extra blood or from holding the extra blood in. When this happens, the penis stays soft. Or the penis gets hard but won’t stay hard. This is called erectile dysfunction (ED).