What Is Atopic Dermatitis?
Atopic dermatitis (a type of eczema) causes chronic (ongoing) skin irritation. This condition can affect people of all ages. It often runs in families. (This means it can be genetic). It may also be linked to allergies, such as hay fever and sometimes asthma. Common symptoms are itching, dry, and red and scaly skin. Atopic dermatitis is not contagious, so it cannot be spread from person to person.
You can help control symptoms by practicing good self-care.
-
Stay away from anything that causes flare-ups, such as sunburn or vigorous scratching.
-
Use fragrance-free thick creams or ointments as part of your daily skin care.
-
Stay away from foods that set off your symptoms.
-
Wash all your clothes (especially when new) with a mild detergent with unscented fabric softener.
-
When you go outdoors, use plenty of sunscreen and moisturizer.
-
Stay away from activities that cause excessive or abnormal sweating.
Where do you have symptoms?
Atopic dermatitis symptoms can appear anywhere on the body. But in most cases, they vary based on the person’s age.
-
In babies, irritated skin or a red rash is often seen on the scalp, cheeks, and chin, near the mouth, and under the eyelids. The rash may ooze when scratched. Infants rarely have atopic dermatitis in the diaper area, but they can get diaper rash from other causes.
-
In children ages 2 through 10, a red thickened rash will be seen most commonly in:
-
In children 11 and older and in adults, symptoms can affect many areas. A red to dark brown scaly rash that may bleed and crust when scratched will appear on:
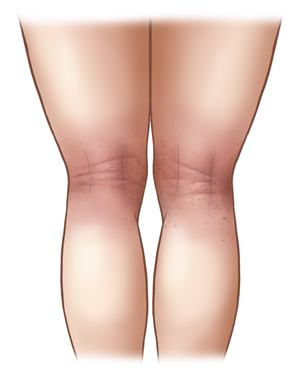 |
| Eczema on light skin. |
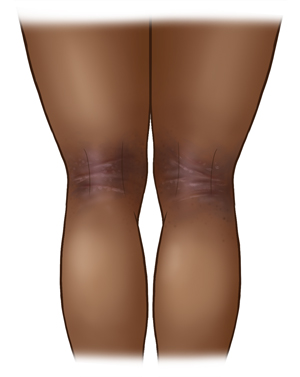 |
| Eczema on dark skin. |
What sets off symptoms?
Symptoms flare because of many things. These include skin dryness, scratching, stress, harsh soaps, and irritants, such as dust or wool.
Try to stay away from anything that causes flare-ups.
Recognizing what causes flare-ups
To figure out what causes atopic dermatitis to flare, work with your health care provider by keeping a list of things (triggers) that seem to irritate your skin. Start by filling in the spaces below. Then keep writing them down in a notebook or diary. The things that affect each person vary. So keep your own list, and try to stay away from your triggers.
_________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________