When Your Child Needs a Modified Barium Swallow
A modified barium swallow is a test used to check your child’s ability to swallow. It's also called a video fluoroscopic swallowing exam, speech swallowing exam, or an oropharyngeal motility study. Barium is used during the test. This is a substance that makes organs show more clearly on X-rays. This test may be advised if your child has problems swallowing food. Problems may include wheezing, choking, or aspiration (when food or liquid goes into the lungs). This test can also check if your child is ready to move from tube feeding to oral feeding. The image part of the test takes about 15 to 20 minutes.
Before the test
Here is what you will need to do:
-
Don’t give your child anything to eat or drink 4 to 6 hours before the test. Talk with the healthcare provider if medicines need to be taken.
-
Follow all other instructions from the healthcare provider.
Let the technologist know
For your child’s safety, let the technologist know if your child:
During the test
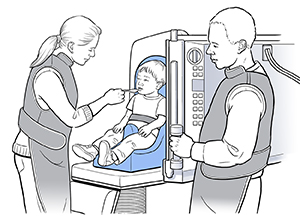 |
| Your child is given barium-coated foods and liquids to swallow and an X-ray video is taken. |
A modified barium swallow is done by a speech pathologist or feeding specialist. These are healthcare providers with training to help people with swallowing or feeding problems. A radiologist is also present. This is a healthcare provider trained to use X-rays to test and treat patients:
-
You can stay in the X-ray room and can help by feeding your child. You’re given a lead apron to wear for your safety. Pregnant women aren’t allowed in the X-ray room.
-
The X-ray table is set upright. Your child is seated in a special chair that is placed against the X-ray table.
-
Your child is given foods and liquids of different textures to swallow. This may include thin liquids such as water; thick liquids such as milk; or thick foods such as pudding. The foods and liquids are coated with barium. Your child may not like the taste of the barium.
-
The speech pathologist or feeding specialist watches your child’s swallowing. Your child is checked for any signs of problems as each food or liquid is swallowed.
-
An X-ray video recording is also taken of your child’s upper GI (gastrointestinal) tract as each food or liquid is swallowed.
After the test
Here is what to expect:
-
The X-ray video and notes from the test are studied. You’ll be advised about what foods or liquids are safe for your child.
-
Your child may not be ready to swallow foods yet and may need to be fed by another method. Your child’s healthcare provider will tell you more if this is needed.
-
If your child can drink liquids, drinking water helps ease constipation that may happen after the test. Call your healthcare provider if your child doesn't have a bowel movement after 24 hours.
-
Your child’s stool may look chalky white or light for 1 to 2 days due to the barium. If no barium is passed in 24 hours, call the healthcare provider.
Helping your child get ready
You can help your child by preparing in advance. How you do this depends on your child’s needs:
-
Explain the test to your child in brief and simple terms. Younger children have shorter attention spans, so do this shortly before the test. Older children can be given more time to understand the test in advance. It may help your child to know that you may be doing the feeding during the test. You may even be allowed to bring samples of food that you know your child likes.
-
As best you can, describe how the test will feel. Allow your child to ask questions.
-
Use play when helpful. This can include role-playing with a child’s favorite toy or object. It may help older children to see pictures of what happens during the test.
Possible risks
These include:
-
Allergic reaction to barium. This includes hives, itching, and wheezing.
-
Aspiration
-
Constipation and bowel obstruction from retained barium
-
Radiation exposure from X-rays
© 2000-2025 The StayWell Company, LLC. All rights reserved. This information is not intended as a substitute for professional medical care. Always follow your healthcare professional's instructions.